Chapter 7. Useful libraries
In this chapter, we’ll cover two third-party libraries. The first one lets you use aspect-oriented programming inside an Android application. The second is a game framework. We’ll walk through what’s possible when you add them to your application.
Have you ever tried to add analytics, ads, and logs to an Android Activity? If you have, you know that your class can get polluted with a lot of code that has nothing to do with your Activity’s logic. In this hack, you’ll see how to solve this issue using aspect-oriented programming (AOP). As an example, we’ll add a log statement to the Activity’s onCreate() method using AOP to make sure that the Activity doesn’t get polluted.
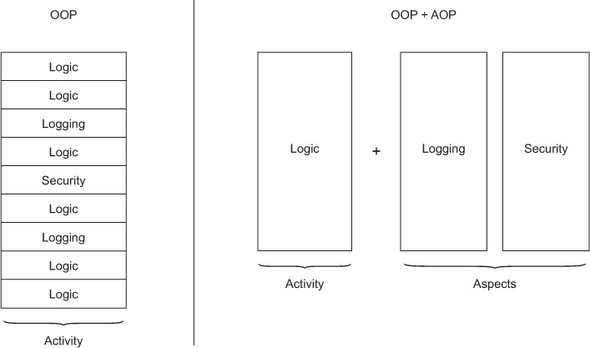
Aspect-oriented programming is a programming paradigm that aims to increase modularity by allowing the separation of cross-cutting concerns. Here’s a basic idea of how all of this works: we specify our cross-cutting concerns in a separated module (aspect), and we place the code that we want to be executed (either before or after our cross-cutting concern) in the separate module or modules. Figure 31.1 illustrates this concept.