Chapter 15. Queuing and stream processing: Illustration
This chapter covers
- Using Apache Storm
- Guaranteeing message processing
- Integrating Apache Kafka, Apache Storm, and Apache Cassandra
- Implementing the SuperWebAnalytics.com uniques-over-time speed layer
In the last chapter you learned about multi-consumer queues and the Storm model as a general approach to one-at-a-time stream processing. Let’s now look at how you can apply these ideas in practice using the real-world tools Apache Storm and Apache Kafka. We’ll conclude the chapter by implementing the speed layer for unique pageviews for SuperWebAnalytics.com.
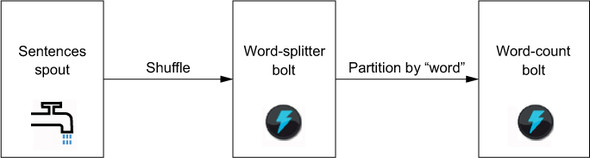
Apache Storm is an open source project that implements (and originates) the Storm model. You’ve seen that the core concepts in the Storm model are tuples, streams, spouts, bolts, and topologies. Let’s now implement streaming word count using the Apache Storm API. For reference, the word-count topology is repeated in figure 15.1.
To begin, you first instantiate a TopologyBuilder object to define the application topology. The TopologyBuilder object exposes the API for specifying Storm topologies:
Next, you add a spout that emits a stream of sentences. This spout is named sentence-spout and is given a parallelism of 8, meaning 8 threads will be spawned across the cluster to execute the spout: