chapter eleven
11 Monitoring and explainability
This chapter covers
- Setting up monitoring and logging for ML Applications
- Routing alerts using Alertmanager
- Storing logs in Loki for scalable log aggregation and querying
- Identifying data drift
- Using model explainability to understand how the ML model makes its decisions
Moving models to production is only the first step - keeping them performing reliably over time requires robust monitoring and understanding of their behavior. In this final chapter, we'll explore how to implement comprehensive monitoring for ML systems and gain insights into their decision-making processes (Figure 11.1).
Figure 11.1 The mental map where we are now focusing on model monitoring(8)
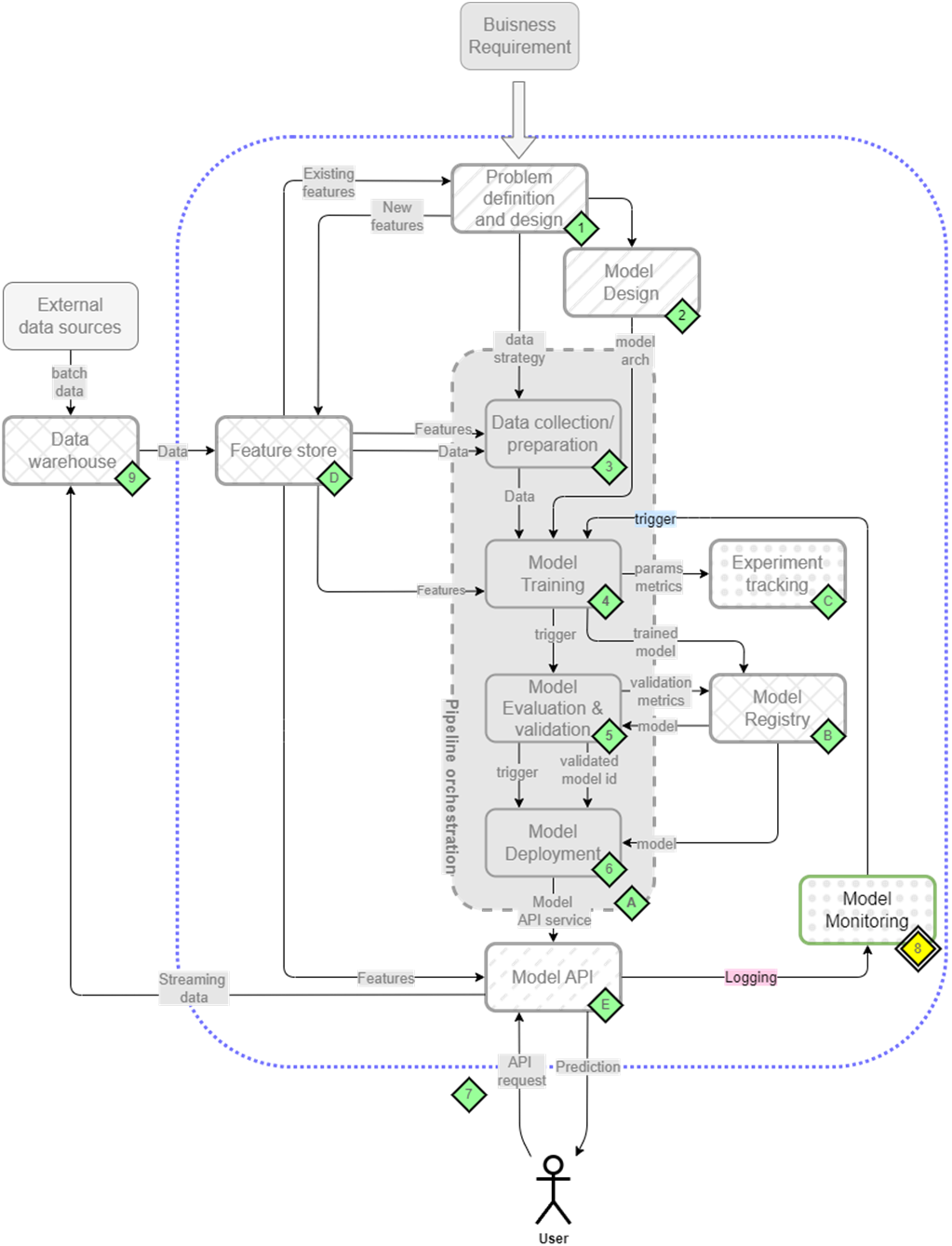
We'll tackle monitoring from two critical angles. First, we'll set up basic operational monitoring to ensure our services meet performance and reliability requirements. Then, we'll implement ML-specific monitoring to detect data drift and track model behavior.
Model monitoring can be split up into two main components.
- Basic monitoring
- Data drift monitoring