chapter two
2 Generating text with a pre-trained LLM
This chapter covers
- Setting up the code environment for working with LLMs
- How to use a tokenizer to prepare input text for an LLM
- The step-by-step process of text generation using a pre-trained LLM
- Caching and compilation techniques for speeding up LLM text generation
In the previous chapter, we discussed the difference between conventional large language models (LLMs) and reasoning models. Also, we introduced several techniques to improve the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. These reasoning techniques are usually applied on top of a conventional (base) LLM.
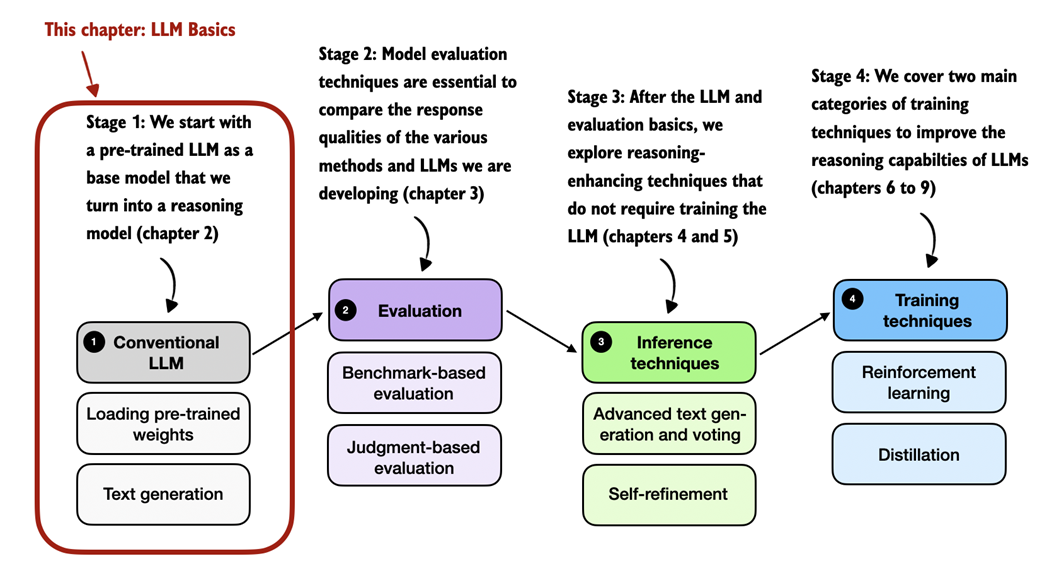
In this chapter, we will lay the groundwork for the upcoming chapters and load such a conventional LLM on top of which we can apply reasoning techniques in subsequent chapters, as illustrated in figure 2.1. This conventional LLM is an LLM that has already been pre-trained to generate general texts (but it has not been specifically trained or enhanced for reasoning).
Figure 2.1 A mental model depicting the four main stages of developing a reasoning model. This chapter focuses on stage 1, loading a conventional LLM and implementing the text generation functionality.