chapter four
4 Improving reasoning with inference-time scaling
This chapter covers
- Prompting an LLM to explain its reasoning to improve answer accuracy
- Modifying the text generation function to produce diverse responses
- Improving reasoning reliability by sampling multiple responses
Reasoning performance and answer accuracy can be improved without retraining or modifying the model itself. These methods operate during inference, when the model generates text. As shown in the overview in figure 4.1, in this chapter, we cover two inference-time scaling methods. As we will see later in this chapter, both methods more than double the accuracy of the base model we used in previous chapters.
Figure 4.1 A mental model of the topics covered in this book. This chapter focuses on techniques that improve reasoning without additional training (stage 3). In particular, it extends the text-generation function and implements a voting-based method to improve answer accuracy. The next chapter then introduces an inference-time scaling approach where the model iteratively refines its own answers.
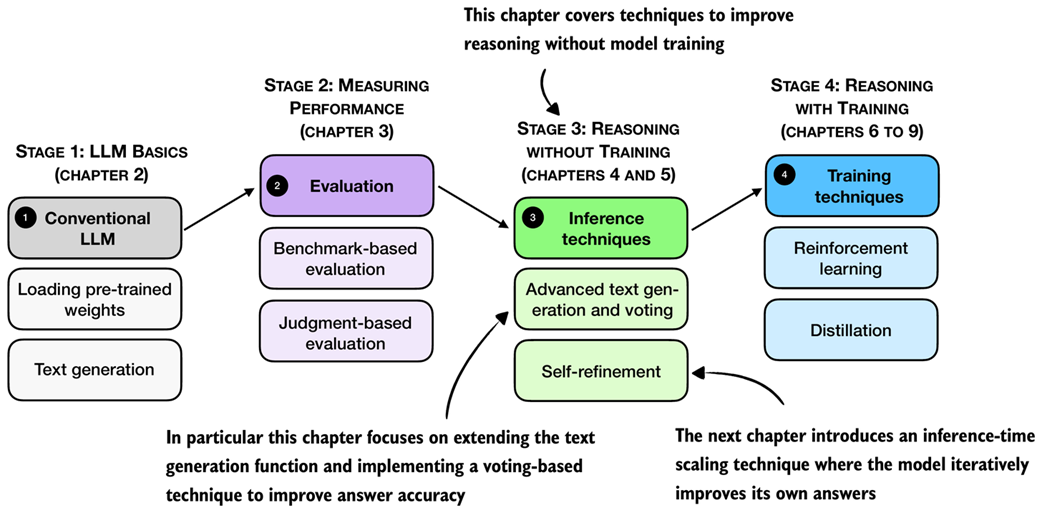
The next section provides a general introduction to inference-time scaling before discussing the inference methods that are shown in figure 4.1 in more detail.
4.1 Introduction to inference-time scaling
In general, there are two main strategies to improve reasoning:
- Increasing training compute and
- increasing inference compute (also known as inference-time scaling or test-time scaling).