5 Inference-time scaling via self-refinement
This chapter covers
- Scoring LLM answers with a simple rule-based scorer
- Computing an LLM's own confidence in its answers
- Coding a self-refinement loop where the LLM iteratively improves its answers
The previous chapter introduced the concept of inference-time scaling (inference scaling for short), which improves the model response accuracy without further training the model. In particular, the focus of the previous chapter was on self-consistency, where the model generates multiple answers, and the final answer is chosen by majority vote.
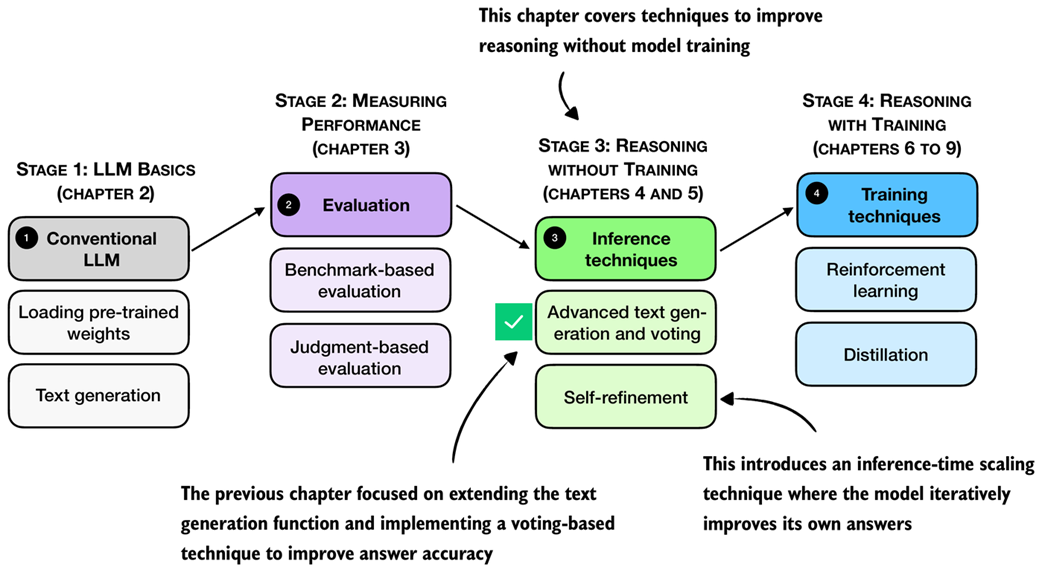
As outlined in figure 5.1, this chapter moves beyond the simple majority voting for inference scaling and covers another popular and useful inference-scaling technique, self-refinement. Instead of generating multiple answers to choose from, self-refinement focuses on iteratively refining a single answer to correct potential mistakes.
Figure 5.1 A mental model of the topics covered in this book. This chapter continues stage 3 and focuses on inference-time techniques for improving reasoning without additional training. This chapter introduces self-refinement, where the model iteratively critiques and improves its own answers.
5.1 Scoring and iteratively improving model responses
As discussed in the previous chapter, inference scaling provides a way to trade additional compute for better accuracy. We also covered two inference scaling techniques, chain-of-thought prompting and self-consistency.