6 Training reasoning models with reinforcement learning
This chapter covers
- Training reasoning LLMs as a reinforcement learning problem with task-correctness rewards
- Sampling multiple responses per prompt to compute group-relative learning signals
- Updating the LLM weights using group-based policy optimization for improved reasoning
Reasoning performance and answer accuracy can be improved by both increasing the inference compute budget and by specific model training methods. This chapter, as shown in figure 6.1, focuses on reinforcement learning, which is the most commonly used training method for reasoning models.
Figure 6.1 A mental model of the topics covered in this book. This chapter focuses on techniques that improve reasoning with additional training (stage 4). Specifically, this chapter covers reinforcement learning.
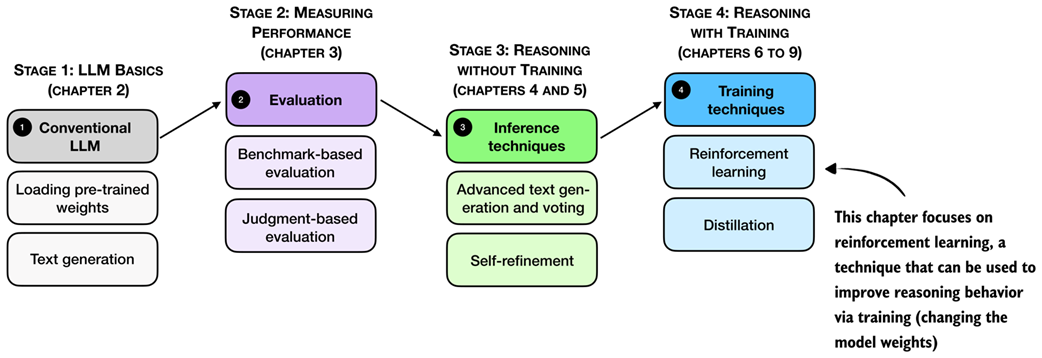
The next section provides a general introduction to reinforcement learning in the context of LLMs before discussing the two common reinforcement learning approaches used for LLMs.
6.1 Introduction to reinforcement learning for LLMs
Inference-time scaling and training-time scaling are two distinct approaches for improving the reasoning performance of large language models, as illustrated in figure 6.2. Inference-time scaling increases accuracy by spending more computation per generated answer, whereas training-time scaling improves accuracy by investing additional computation during training. This chapter focuses on training-time scaling.