2 The brain of AI agents: LLMs
This chapter covers
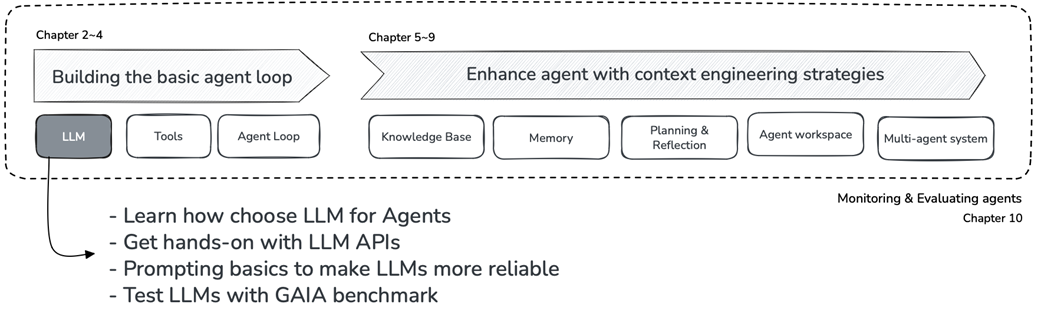
- Selecting the right LLM for agent development
- Using LLM APIs with LiteLLM
- Prompt engineering for agents
- Experiencing LLM limitations through the GAIA benchmark
Throughout this book, we'll build a Research Agent, a system that can interpret requests like "survey recent work on X" or "extract key findings from these PDFs," gather information from multiple sources, and synthesize findings into comprehensive answers. At the heart of this agent lies the LLM, serving as its decision-making brain. But before we can build an effective agent, we need to answer some fundamental questions: Which LLM should we use? How do we communicate with it programmatically? And crucially, what can an LLM do on its own, and where does it fall short?
We’ll address these questions head-on, starting with exploring how to choose an LLM for agent development, then get hands-on with APIs using LiteLLM to work seamlessly across providers. We'll examine prompt engineering principles that transform a general-purpose LLM into a reliable agent. Finally, we'll put LLMs to the test using the GAIA benchmark, directly experiencing their limitations when faced with real-world problems. This experiment will reveal exactly why agents need tools, setting the stage for everything we build in chapter 3 and beyond.
Figure 2.1 Journey through the book – Chapter 2 in focus