appendix B More about quantum states and gates
B.1 The Bloch sphere
A qubit (and, more generally, a pair of amplitudes) can be illustrated using the three-dimensional Bloch sphere, shown in figure B.1. In this book, we do not rely on the Bloch sphere for visualizing single-qubit states. However, you may find it helpful for building intuition.
Figure B.1 The Bloch sphere
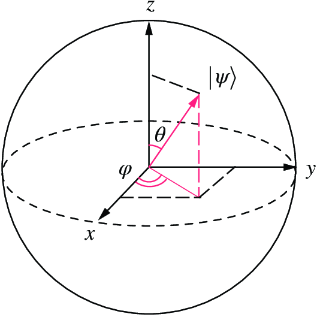
A single-qubit state with probability p = cos2 θ/2 of the outcome 0 can be written in Ket notation as
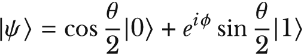
where 0 ≤ φ < 2π.
We can get to this form by starting with a state in the general form:
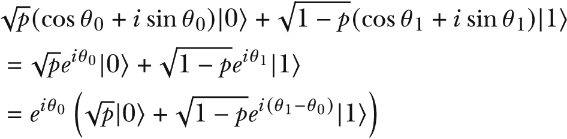
Using an angle 0 ≤ θ < π such that p = cos2 θ/2, and therefore 1 – p = sin2 θ/2, we arrive at this expression:
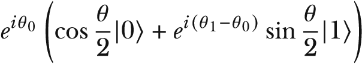
This is the same as the Bloch sphere representation, which ignores the factor 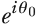 , called a global phase.
, called a global phase.
Let’s use a Bloch sphere to visualize the example single-qubit state where the probability of outcome 0 is p = 0.35 and the directions of the amplitudes are θ0 = 60° = π/3 and θ1 = 120° = 2π/3. We can express the state with the following equation:
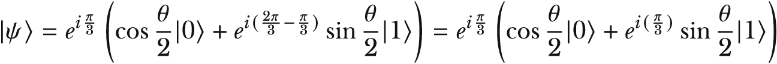
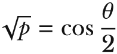 , and therefore
, and therefore 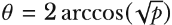 .
.