4 How Machine Learning and Causal Inference can help each other
This chapter covers
- What are we actually estimating when we use machine learning models?
- When to use causal inference and when to use machine learning
- How to use machine learning models in the adjustment formula
you are here
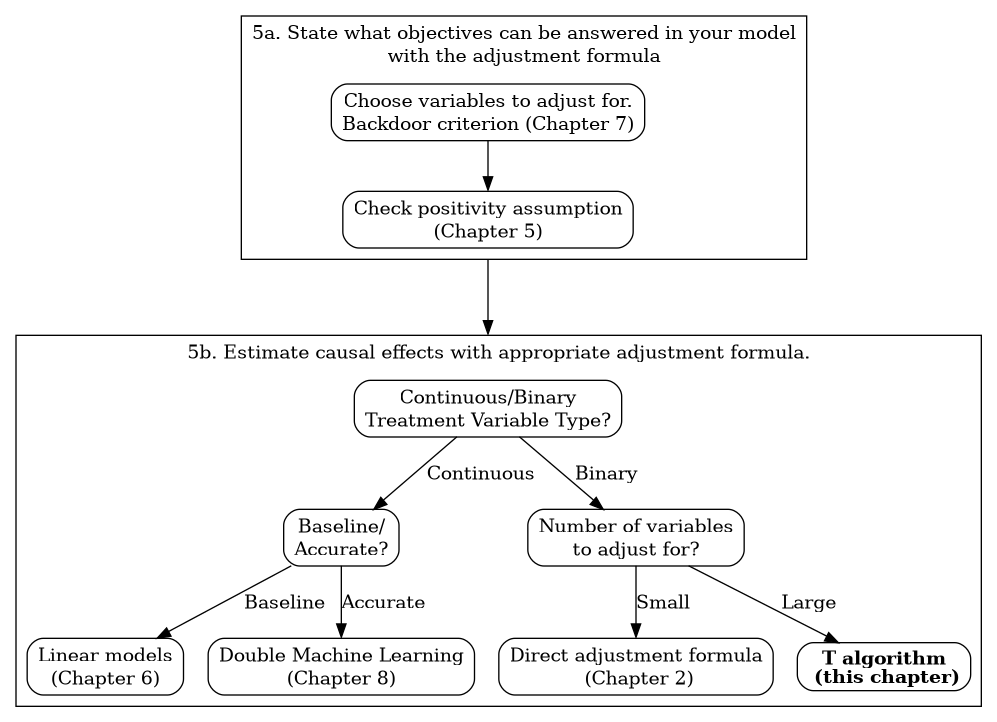
Figure 4.1 Applying the adjustment formula
In the last decade we have seen an explosion of applications of machine learning in a wide variety of domains. It has become a very popular tool and we keep on seeing new advances every day. These advances, such as automatic translation or self-driving cars, have been so astonishing, especially in areas related to image, video, audio and text, that sometimes it may seem that machine learning is the definitive solution to mimic human intelligence. In fact, this has been the main goal of Artificial Intelligence (AI), an area that combines a wide range of techniques, from logic to robotics. Currently, AI has seen in machine learning a huge potential and has invested a lot of resources in it. However, as with any other tool, machine learning also has its limitations. One of them, as we will see in this chapter, is that it doesn’t handle causality well on its own. So, if AI ever wants to fully develop its potential, at some point it will have to also include causal inference techniques.