2 Cybersecurity analytics toolkit
This chapter covers
- Key components of a cybersecurity toolkit
- Choosing the right tools
- Designing insightful dashboards
- Statistical analysis for threat detection
- Integrating AI in security analytics
A cybersecurity analytics toolkit consists of multiple integrated tools working together to support various stages of security analytics. The main components for any specific scope, include data collection, processing, visualization, and automation. Each of these tools plays a role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of security teams. We can visualize this as in figure 2.1 showing how each toolkit is made up of various parts all within the defined scope.
Figure 2.1 Cybersecurity toolkit consisting of the proper scope, tool selection, data collection, processing, visualization, and automation.
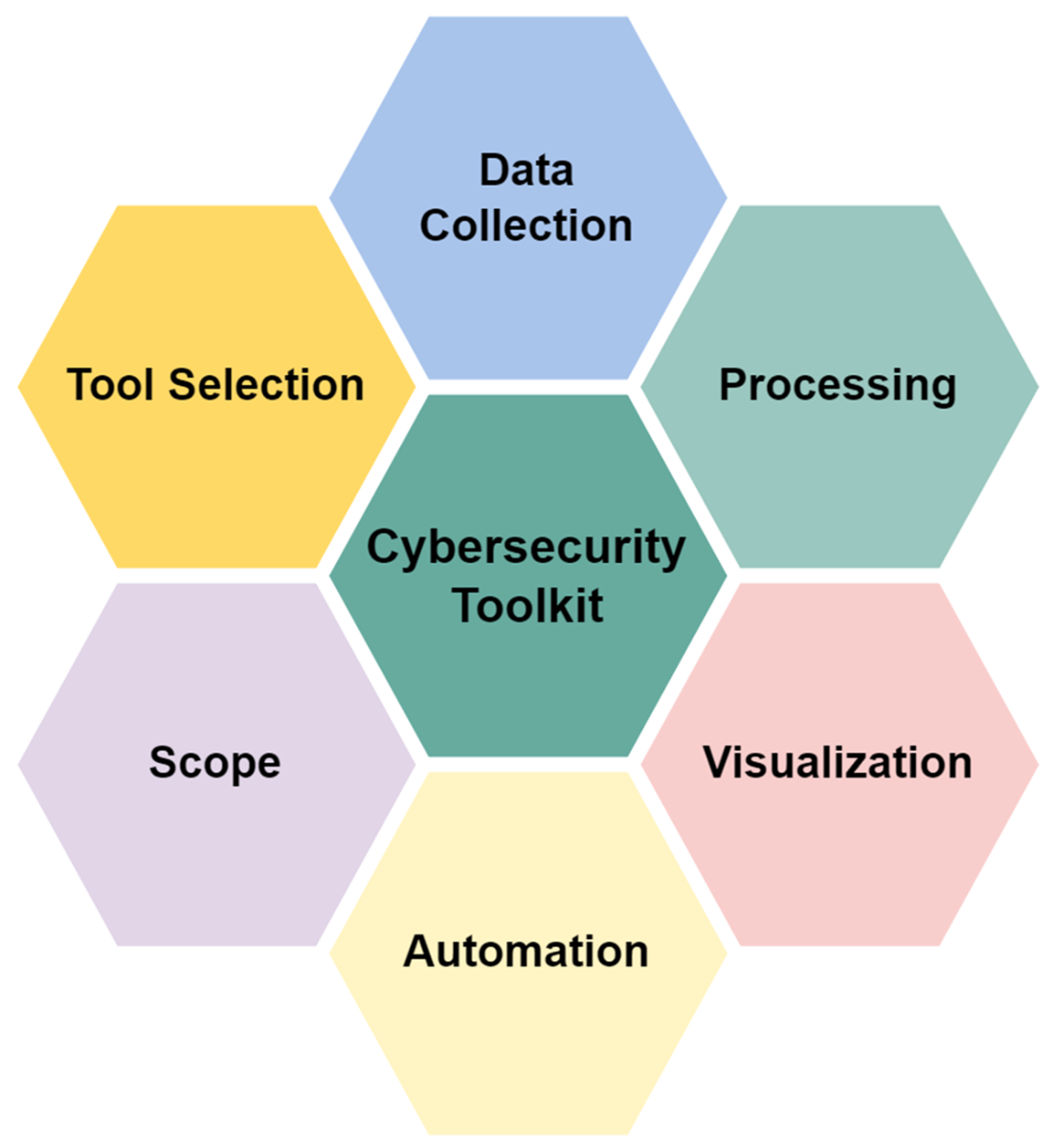
Data collection involves the gathering of data from various sources such as logs, network traffic, and endpoint activity. Tools such as SIEMs and IDSs are typically used for this purpose. Once collected, the data must be processed and normalized for analysis. This process involves parsing, enriching, and correlating data to make it suitable for deeper investigation and interpretation. With large volumes of data, it is important to have visualization tools to help display complex information in easy-to-understand formatting. Dashboards and graphs are commonly used to highlight trends, anomalies, and security events.