3 Text embeddings
This chapter covers:
- The preparation of texts for deep learning purposes, using word and document embeddings.
- Benefits and drawbacks of self-developed text embeddings and pre-trained embeddings developed by others.
- Word similarity with word2vec.
- Document retrieval via document embeddings, using doc2vec.
This diagram shows the organization of the chapter:
Figure 3.1. Chapter organization.
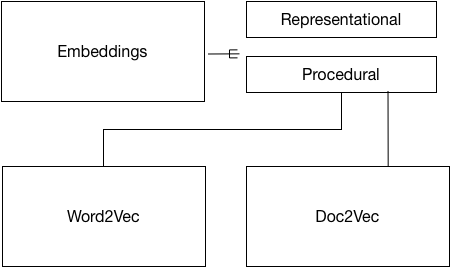
After reading this chapter, you will have a practical command of text embedding algorithms, and you will have developed insight into how to use embeddings for NLP. We will go through a number of concrete scenarios to reach that goal.
But first, let’s review the basics of embeddings.
Figure 3.2. There are different types of mbeddings: Representational and Procedural.
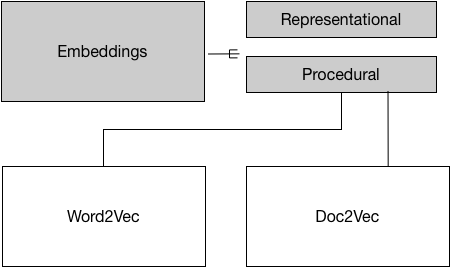
Embeddings are procedures for converting input data into vector representations. A vector is a container (like an array) containing numbers. Every vector lives in a multidimensional vector space, as a single point. Embeddings are systematic, well-crafted procedures for projecting ('embedding') input data into such a space.
We have seen ample vector representations of texts in Chapter 1 and Chapter 2, such as one-hot vectors (binary-valued vectors with one bit 'on' for a specific word), used for bag-of-word representations, frequency-based vectors, and word2vec representations. All these vector representations were created by embeddings.