Appendix C. Detect fake insurance claims using different implementations of gradient-boosted trees
This appendix covers
- Analyzing fake insurance claims dataset
- Building gradient-boosted trees (GBT) models
- Comparing GBT implementations – scikit-learn, XGBoost, LGBM, CatBoost
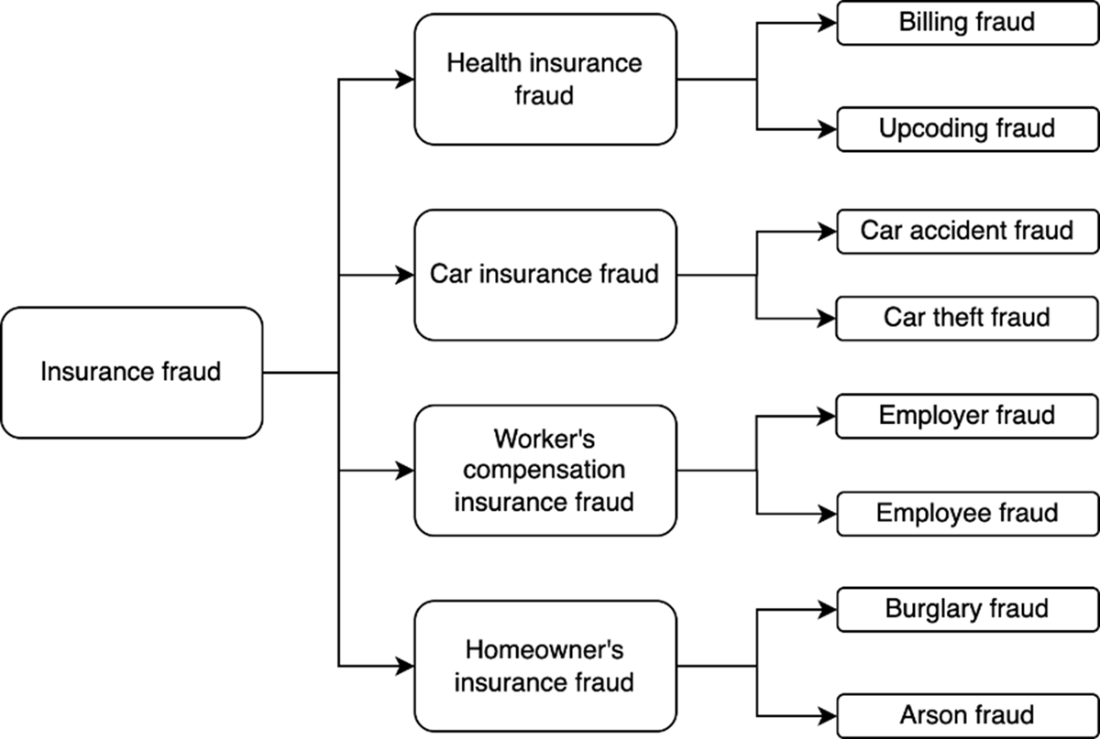
There is a good chance that you have bought at least one insurance – be it health insurance, car insurance, life insurance, or something more specific. Insurance has a buyer (you), a seller (an insurance company), and an intermediary (hospitals in the case of health insurance for example). Insurance fraud is an illegal act committed by the buyer, seller, or intermediary of an insurance. While you may be a genuine insurance buyer, there are plenty of fraudsters out there, making insurance fraud a multi-billion-dollar industry. According to the Coalition Against Insurance Fraud (https://insurancefraud.org/wp-content/uploads/The-Impact-of-Insurance-Fraud-on-the-U.S.-Economy-Report-2022-8.26.2022.pdf), insurance fraud cost the US $308.6bn annually in 2022. Insurance fraud takes various shapes and forms as shown in figure C.1.
Figure C.1 Most common types and sub-types of insurance fraud.