12 Credit card fraud detection using logistic regression
This chapter covers
- Understanding credit card fraud with data
- Building a logistic regression-based fraud detection model
- Interpreting trained logistic regression model
- Deploying an ML model as a service
By 2022, the number of Americans falling victim to credit card fraud had risen to over 151 million, representing approximately 65% of all American cardholders—an increase from 127 million individuals in 2021 (https://www.security.org/digital-safety/credit-card-fraud-report/). This rise in credit card fraud shows both the prevalence of, as well as a steady increase in credit card fraud cases. The median fraud charge from such attacks has also increased from USD$62 in 2021 to USD$79 in 2022. As we are increasingly using cards for payments and integrating card payment solutions with all kinds of businesses, it becomes a necessity to build robust credit card fraud detection systems.
Figure 12.1 Different types of credit card fraud.
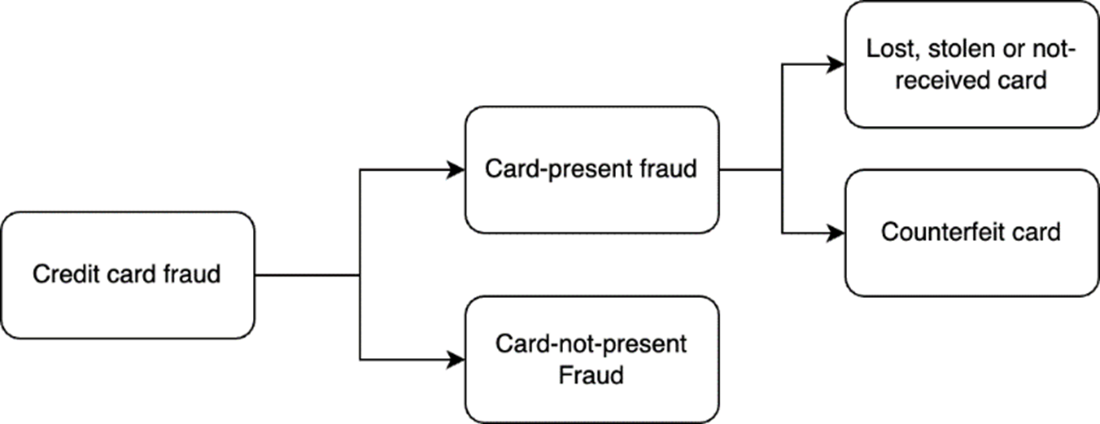
Credit card fraud refers to any unauthorized use of a credit/debit card for fraudulent purposes. Credit card fraud takes different shapes and forms. Here are some broad types of credit card fraud: