This chapter covers
- Propagating cancellation signals using the
contextpackage - Efficiently processing HTTP using the
net/httppackage - Efficiently consuming byte streams using the
iopackage - Understanding Go’s interface embedding and composition mechanics
- Employing idiomatic testing techniques using the
RoundTripperinterface - Testing against a test HTTP server using the
httptestpackage
Using Go involves more than learning basic language mechanics. The path to fully grasping it also involves effective use and understanding of the patterns and techniques in its standard library. Rather than learn from isolated code snippets that provide a limited view of Go’s capabilities, we’ll continue to apply Go to projects that closely resemble real-world ones.
7.1 Revisiting the concurrent pipeline
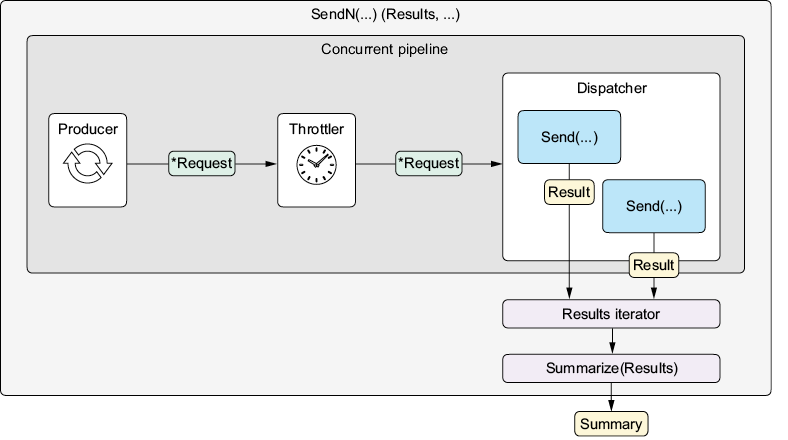
Chapter 6 focused on designing a synchronous API for the hit package and structuring concurrent code using the concurrent pipeline pattern. Figure 7.1 shows how the pipeline operates. The SendN function returns a Results iterator that sends concurrent requests using the Send function and pushes each Result to consumers. The convenience function, Summarize, consumes each Result from the iterator and produces a Summary.
Figure 7.1 SendN runs a concurrent pipeline that simulates sending requests using Send. It returns a Results iterator that pushes each Result from the pipeline to consumers. Summarize consumes the iterator and produces a Summary.