Appendix C. XML and Spring builders
Groovy allows you to easily generate XML using the groovy.xml.MarkupBuilder class. We’ll show you the basic mechanics of that class and then look at how Spring’s XML configuration format maps to the bean builder syntax used in chapter 14, because the mapping is similar.
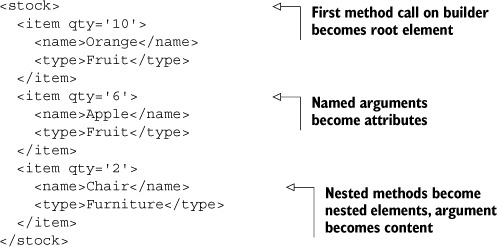
Generating XML text is trivial with the MarkupBuilder class. We’ll demonstrate with a simple example, as shown in the following listing.
This ability to convert method calls into elements and named arguments into attributes makes it easy to generate XML, particularly when you factor in loops and conditions.
Note
MarkupBuilder doesn’t work with static type checking.
Grails’s Bean Builder for Spring maps to Spring XML in a similar fashion to MarkupBuilder syntax and XML but with key differences. Much of the information about Spring on the web is based on XML configuration, so it’s important that you know how to map the XML to Bean Builder syntax. This section explains how that mapping works.