chapter eleven
Let’s start this new topic by considering the most common applications that deal with natural language (in different format) for providing services to end users. You likely use them every day, probably without even noticing how complex and useful they are.
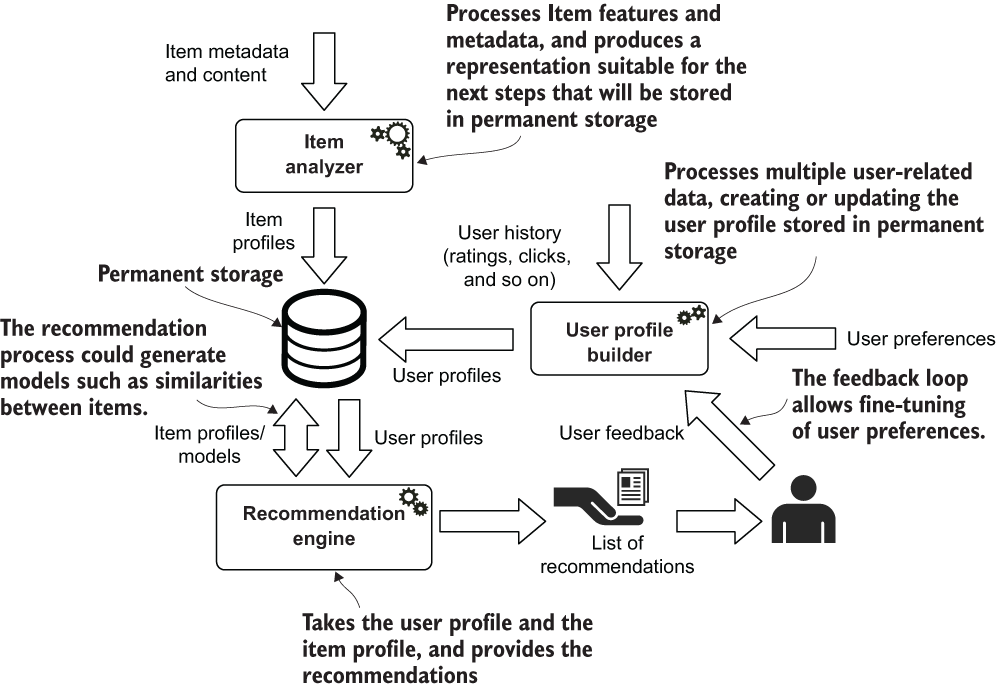
Chapter 4 dealt with text to implement a recommendation engine that uses the content related to the items, such as the description of a product or a movie plot. In that case, this data was used to compare items or user profiles, find commonalities (specifically, similarities) among users or items, and use them to suggest something that might be of interest to the current user. Figure 11.1 presents the high-level structure of a content-based recommendation engine taken from chapter 4.