Chapter 5. Understanding controllers and services
This chapter covers
- Controllers and their responsibilities
- Services
- Metaprogramming and inspection capabilities on artifacts
Wading through Griffon’s MVC is quite a journey, but we’re almost done reviewing what it has to offer. The final piece we’ll look at takes care of routing all of the user’s input to and from the appropriate handlers. We’re talking about the brains of your application: the controller member of the MVC triad. In Griffon, this member is mostly represented by controllers; services are also used to a lesser extent.
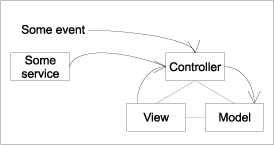
Simply put, controllers have the responsibility to react to inputs, usually coming from the UI. Inputs may also come from other locations, such as a service or an application event (application events will be covered in chapter 8). But regardless of the input’s source, the controller will most likely update the model, which in turn may update the view. Figure 5.1 illustrates the controller reacting to multiple inputs.
Controllers also have the ability to create and destroy other MVC groups, as you saw back in chapter 1. The GroovyEditController creates a new MVC group (FilePanel) for every tab that’s required. The FilePanelController cleans up the group when the tab is disposed.