In this chapter
- reviewing the more complex topics in streaming systems
- understanding where to go from here
“It’s not whether you get knocked down; it’s whether you get up.”
—Vince Lombardi
You did it! You have reached the end of part two of this book, and we have discussed quite a few topics in more detail. Let’s review them quickly to strengthen your memory.
Well, we authors think it’s safe to say this is the end of the book, but you can count on having many more years of learning and experimenting in front of you. As we sit and write this chapter, we’re reflecting on the long journey of learning. What an adventure it has been for us! Hopefully, after reading this book, you feel that you benefited from it—we certainly have.
What you will get from this chapter
There have been many complex topics covered in the second half of the book. We’d like to recap the main points. You may not need to know all of these topics in depth in the beginning of your career, but knowing them will help you establish yourself in the upper echelon of technologists in the field when it comes to real-time systems. After all, learning these topics well is not a trivial task.
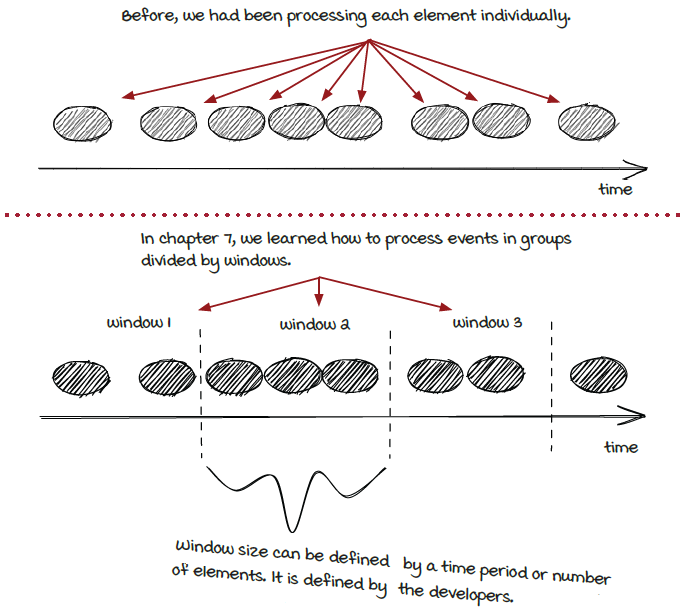
We learned that not all streaming jobs want to handle events one at a time. It can be useful to group events together in some cases, whether that is time- or count-related.