In this chapter
“First, solve the problem. Then, write the code.”
—John Johnson

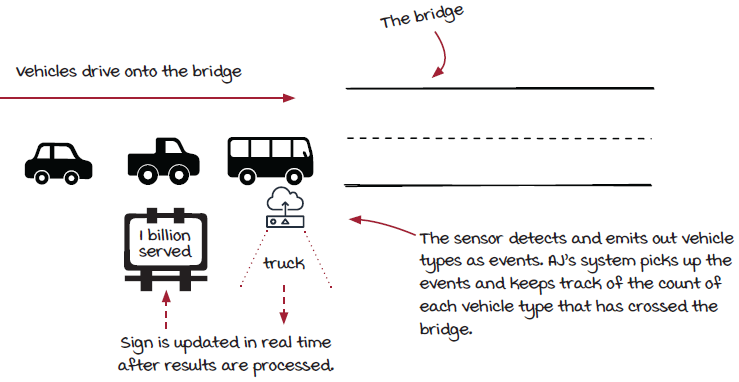
As technology has quickly advanced over the years, most of the manual parts of tollbooths have been replaced with IoT (Internet of Things) devices. When a vehicle enters the bridge, the system is notified of the vehicle type by the IoT sensor. The first version of the system is to count the total number of vehicles by type (cars, vans, trucks, and so on) that have crossed the bridge. The chief would like the result to be updated in real time, so every time a new vehicle passes, the corresponding count should be updated immediately.
AJ, Miranda, and Sid, as usual, started out with the tried and true backend service design that used HTTP requests to transfer data. But it failed.

Traffic increased for the holidays. The system took on a load that it couldn’t handle. The latency of the requests caused the system to fall behind, leading to inaccurate up-to-date results for the chief and a headache for AJ and Miranda.


