5 Delivery Semantics
This chapter covers:
- Delivery semantics and their impact
- Three delivery semantics
- 1. At-most-once delivery semantic
- 2. At-least-once delivery semantic
- 3. Exactly-once delivery semantic
“There’s never enough time to do it right, but there’s always enough time to do it over.”
Jack Bergman
Computers are pretty good at performing accurate calculations. However, when computers working together in a distributed system like many streaming systems, accuracy becomes a little bit more (I mean, a lot more) complicated. Sometimes, we may not want 100% accuracy, because other more important requirements need to be met. “Why do we want wrong answers?”, you may ask. This is a great question and it is the one that we need to ask when designing a streaming system. In this chapter, we are going to discuss an important topic related to accuracy in streaming systems: delivery semantics.
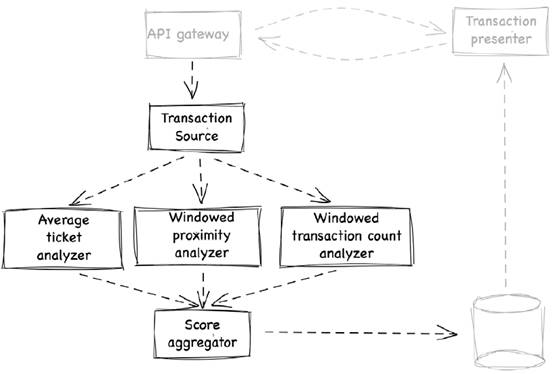
5.1 The latency requirement of the fraud detection system
| In the previous chapter, Tim and Tracy have built a credit card fraud detection system which can make a decision within 20 milliseconds for each transaction and store the result into the database. Now, let’s ask an important question when building any distributed system: what if any failure happens? |
|