7 Windowed computations
In this chapter:
- Standard windowing strategies
- Time stamps in events
- Windowing watermark and late events
The attention span of a computer is only as long as its powercord.
— Unknown
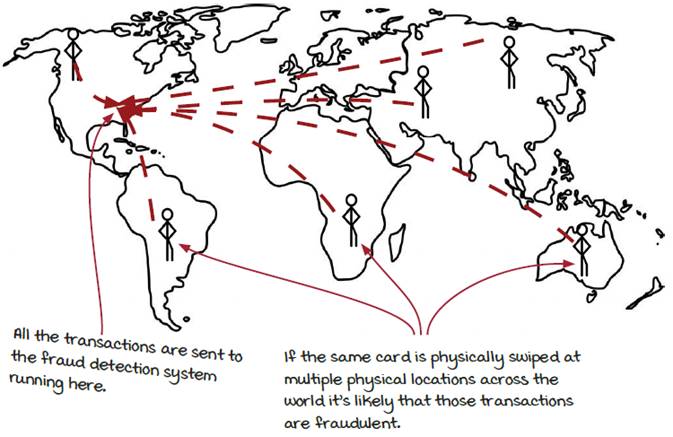
In the previous chapters, we have built a streaming job to detect fraudulent credit card transactions. There could be many analyzers that use different models, but the basic idea is to compare the transaction with the previous activities on the same card. Windowing is designed for this type of work and we are going to learn the windowing support in streaming systems in this chapter.
7.1 Slicing up real-time data
As the popularity of Tim and Tracy’s new product has grown, so has the attention of new types of hackers. A group of hackers has started a new scheme involving gas stations.
Here’s how it works: they capture an innocent victim’s card information and duplicate it across multiple new physical credit cards. From here the attackers will send the newly created fraudulent cards out to others in the group and orchestrate spending money on the same credit card across multiple locations across the world at the same time to purchase gas. They hope that by charging the card all at once, the card holder will not notice the charges until it’s too late. The result is free gas. Why do they go to a global scale to try and get free tanks of gas? We can consider this a mystery.