appendix A Introduction to graphs
Although graphs are simple data structures, it is important to understand how to represent them and to be familiar with the main concepts related to them. This appendix introduces the key elements of the graph world. If you already understand these concepts or have read Alessandro’s previous book [1], from which the following sections were excerpted, you can skip this appendix.
A.1 What is a graph?
The graph is a simple and old mathematical concept. It is a data structure consisting of a set of vertices (or nodes/points) and edges (or relationships/lines) that can be used to model relationships among a collection of objects.
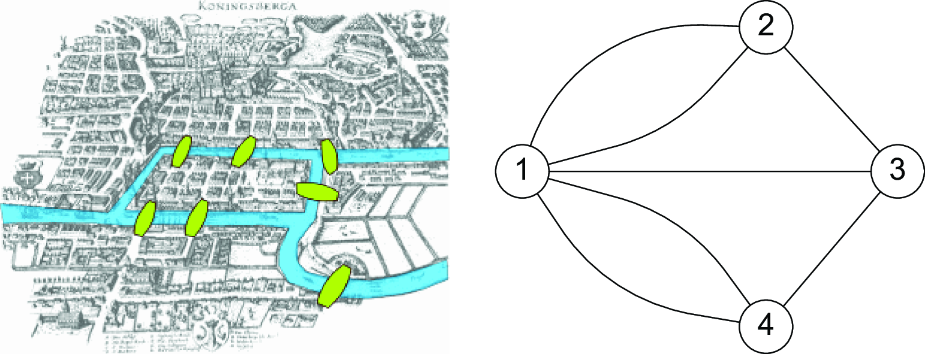
Legend says that it was the lazy Leonhard Euler who first started talking about graphs in 1736. He was visiting Königsberg in Prussia (now Kaliningrad, Russia), which sat on both sides of the Pregel River and included two large islands that were connected to each other and to the two mainland portions of the city by seven bridges. Euler didn’t want to spend too much time walking through the city, so he formalized the problem to cross each bridge once and only once. This led to the invention of graphs and graph theory [2]. He proved that it was an impossible task, and he stayed home instead. Figure A.1 shows an old representation of Königsberg and the related graph representation used by Euler to prove his thesis.
Figure A.1 The bridges in Königsberg, Russia, that led Leonhard Euler to the invention of graph theory in 1736