In the previous chapter, you got to know flows as the higher-level abstraction that allows you to work with multiple, sequential values over time while leveraging Kotlin’s concurrency machinery. In this chapter, we’ll discuss how to manipulate and transform them. You’ve already seen that Kotlin provides a vast selection of operators you can use to manipulate collections (as discussed in chapters 5 and 6). Likewise, you can use operators to transform flows.
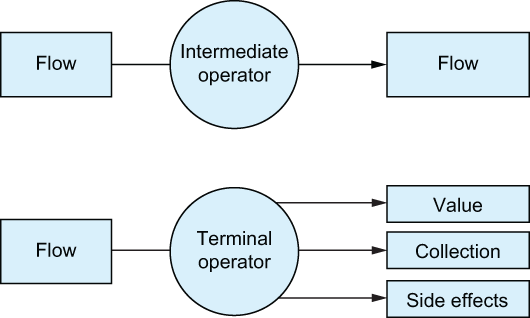
Just like with sequences, you distinguish between the intermediate flow operators and terminal flow operators analogously to our discussion in chapter 6: intermediate operators return another, modified flow, without actually running any of the code yet. Terminal operators return a result—like a collection, an individual element from the flow, a computed value, or no value at all—collecting the flow and executing the actual code (visualized in figure 17.1).