chapter five
5 Using the OpenAI API in Data Workflows
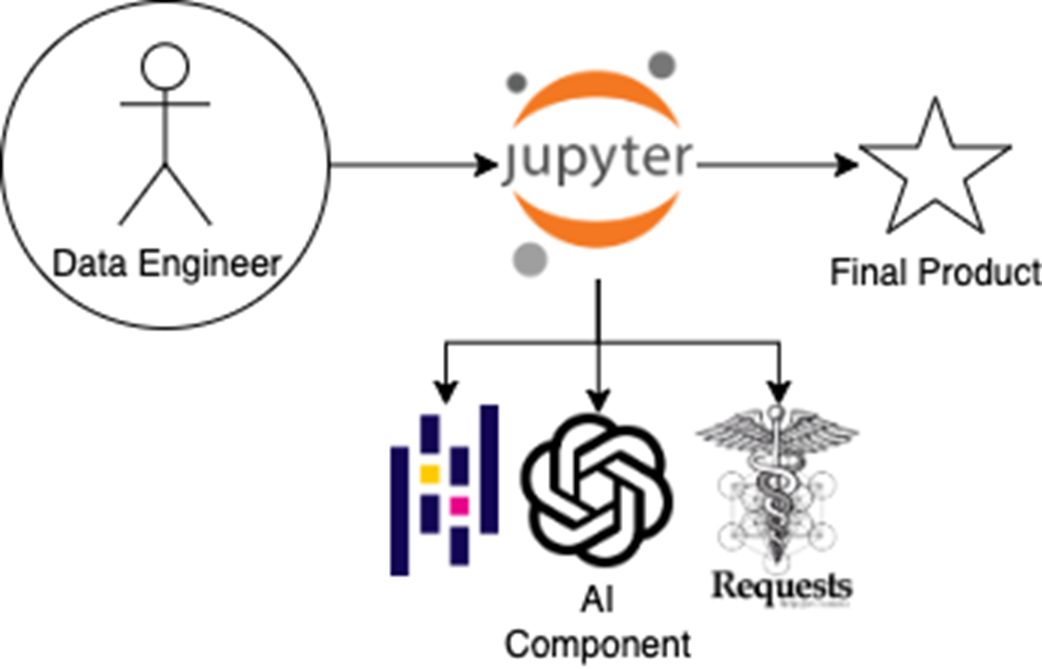
In the last few chapters, you worked alongside an AI coding companion—asking for help in SQL, generating Python scripts, and refining logic through conversational prompts. Now we’re making a subtle but powerful shift: instead of using AI from the outside-in, we’re embedding it within the data pipeline itself. This change marks a new phase in the data engineer’s relationship with AI—one where the model isn’t just an assistant, but a component of the workflow
Figure 5.1 In earlier chapters, the data engineer acted as a go-between—manually passing instructions between an AI coding companion and the coding environment. Now, the AI component is embedded directly within the workflow, alongside libraries like Requests and Pandas, enabling natural language tasks (like sentiment analysis) to execute as native steps within the Jupyter notebook