chapter eight
8 Stream processors for time series calculations and filtering
This chapter covers
- Learning some core ideas about stream analytics
- Querying data streams created by Fluent Bit
- Exploring the SQL-like syntax provided for streaming analytics
- Creating new outputs based on Fluent Bit inputs
Let’s start by orienting ourselves in the Fluent Bit landscape, seeing how this chapter fits into our technology landscape.
8.1 Architectural context
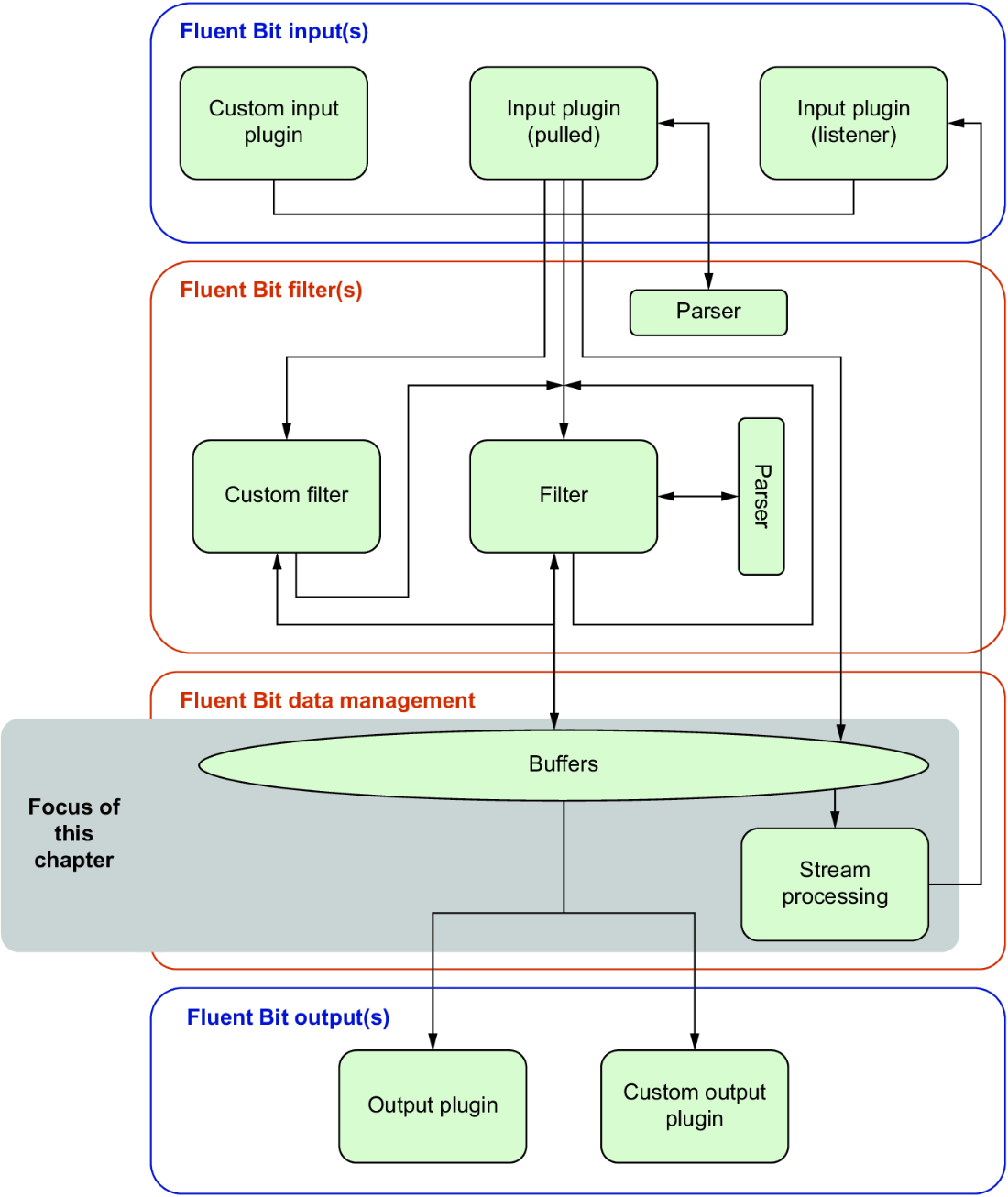
Figure 8.1 gives us some immediate insights into what we can do with streaming, with the flow going back to an input. Similarly, we can output stream-processing results to the relevant output plugins. Before we can look at that, however, we need to understand the key ideas involved.
Figure 8.1 Representation of Fluent Bit from a logical architecture perspective, highlighting the aspects of Fluent Bit that this chapter will address. Here, we’re particularly interested in the buffer and the stream processing that depends on the buffer’s capabilities.
8.2 Key ideas
- We express the logic to be applied using SQL-style syntax.
- Although the syntax is SQL-based, no database is involved. The only data pool available is the buffer.
- Our analogy for tables in the SQL syntax is a stream or a tag, and columns in a relational table are analogous to the log event attributes in the Fluent Bit event.
- We can execute our expressions against streams and tags.