appendix Installing Jenkins on Minikube
This appendix will walk you through the process of running Jenkins on your local Minikube cluster, which we use in the examples in chapter 10.
Running Jenkins on Kubernetes
You can run Jenkins as another service on the local Kubernetes cluster — Minikube — you set up in chapter 9. If you’re working from scratch, follow the installation instructions on GitHub to get Minikube running (https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube). Once you have it installed, bring up the cluster by running minikube start at your terminal.
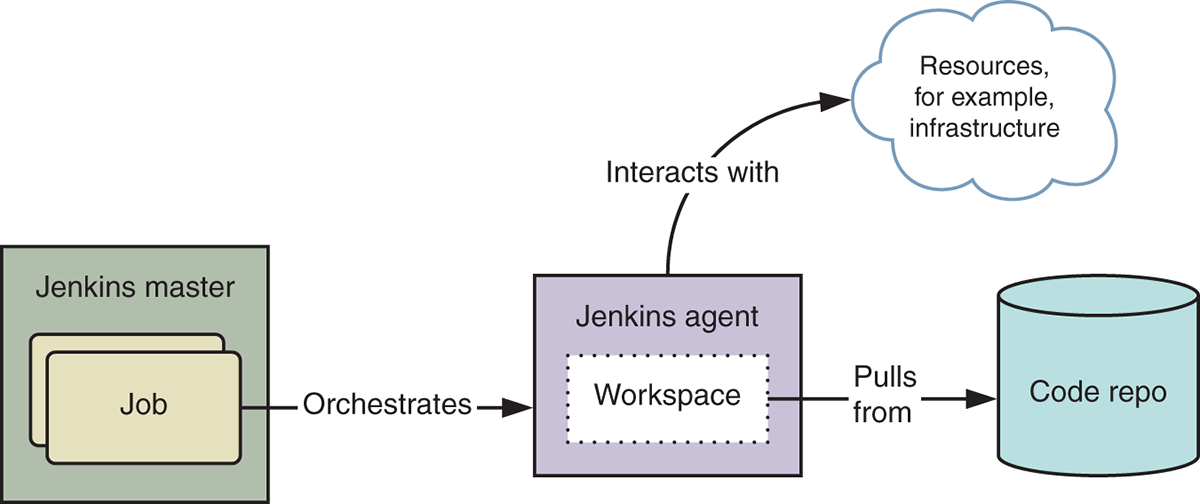
The Jenkins application consists of a master node and, optionally, any number of agent nodes. Running a Jenkins job executes scripts (such as make) across agent nodes to perform deployment activities. A job operates within a workspace — a local copy of your code repository. Figure A.1 illustrates this architecture.
You’ll use Helm to install an “official” Kubernetes-ready configuration of Jenkins on your Minikube cluster.
Figure A.1 A high-level Jenkins architecture
Setting up Helm
You can think of Helm (https://helm.sh/) as a package manager for Kubernetes. Helm’s package format is a chart, which defines a set of Kubernetes object templates. Community-developed charts, like the one you’ll use for Jenkins, are stored on Github (https://github.com/helm/charts).
Helm consists of two components: