2 Building your first multi-agent application
This chapter covers
- Defining agents in code
- Granting agents access to tools
- Implementing short and long term memory in agents
- Exploring strategies for task termination
- Orchestrating groups of agents to address tasks
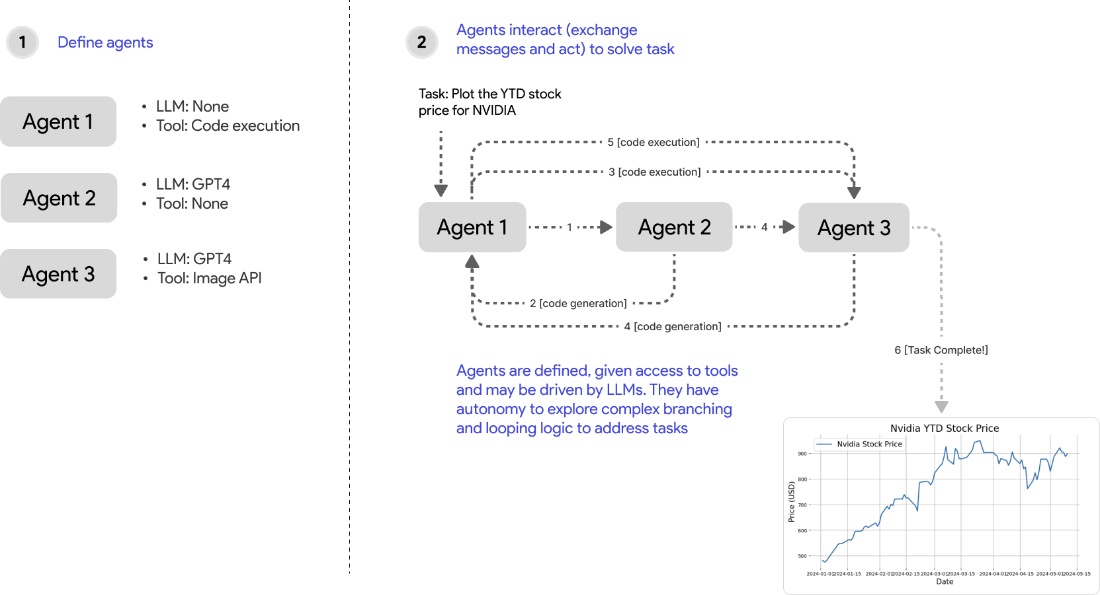
In this chapter, we will cover several key concepts necessary for the implementation of agents, including defining agent capabilities, granting agents access to tools, providing agents with memory, orchestrating their interactions, and establishing strategies for task termination. To demonstrate these concepts, we will illustrate their implementation using the AutoGen library - a Python library that offers a high-level API for building multi-agent applications. We will use a recurring example of creating a group (workflow) of agents employing an autonomous multi-agent collaboration pattern (see Figure 2.1). We will extend this agent workflow and apply them to two high-level tasks (instructions phrased in natural language), such as visualizing stock prices, and generating a detailed pdf catalog for an art exhibition.
Figure 2.1 An application where multiple agents collaborate autonomously to solve a task can be implemented across two main steps. In step 1, we define the agents and their capabilities (e.g., equip them with an LLM for generating responses or tools for acting). In step 2, we orchestrate the agents (exchange messages and act) to solve the task.