6 Using Libp2p for content distribution
This chapter covers
- Understanding peer-to-peer pub/sub systems
- Using the publish and subscribe features of Libp2p to synchronize media
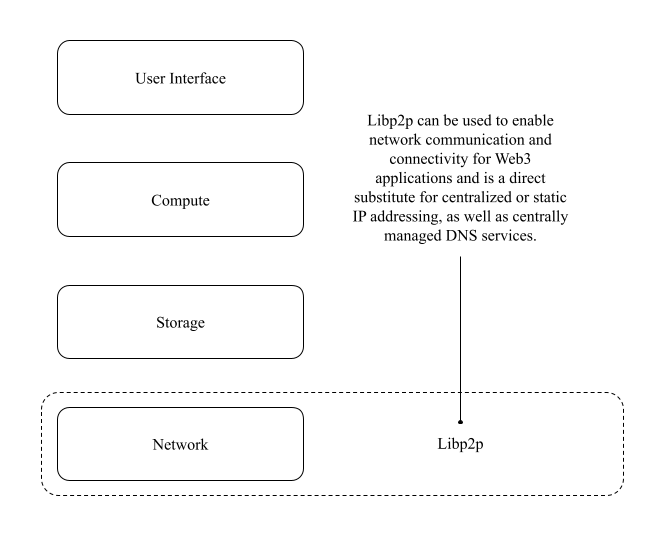
In this chapter, you’ll learn about the publish/subscribe (pub/sub) features of Libp2p. Using publish and subscribe, Web3 application developers allow instances of their application to send and receive messages to each other instead of communicating via a central server. This functionality replaces a central server and allows applications to stay up to date by synchronizing settings and code changes to deliver rich media and other content to users as they connect. To demonstrate this, you will update the Code Radio demo application to allow application instances to synchronize the music catalog to discover songs not in their local library and download those songs from peers. Within the Code Radio application architecture, Libp2p pub/sub communications are part of the base networking layer (figure 6.1).
Figure 6.1 Defining the Web3 application architecture of the Code Radio application starts at the base network layer.