chapter ten
This chapter covers
- Deploying a self-healing Swarm cluster on AWS and using an S3 bucket for node discovery
- Running SSH-based commands within Jenkins pipelines and configuring SSH agents
- Automating deployment of Dockerized applications to Swarm
- Integrating Slack to manage releases and build notifications of CI/CD pipelines
- Continuous delivery to production and user manual approvals within Jenkins
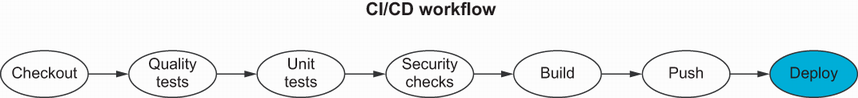
The previous chapter covered how to set up a continuous integration pipeline for a containerized microservice application with Jenkins. This chapter covers how to automate the deployment and manage multiple application environments. By the end of this chapter, you will be familiar with continuous deployment and delivery (figure 10.1) for containerized microservices running in a Docker Swarm cluster.
One of the basic solutions to run multiple containers across a set of machines is Swarm (https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/), which comes bundled with Docker Engine. By the end of this chapter, you should be able to build a CI/CD pipeline from scratch for services running inside a Docker Swarm cluster, as shown in figure 10.2.