chapter three
3 Defining Jenkins Architecture
This chapter covers
- How Jenkins distributed builds work
- The role of Jenkins master and workers nodes
- How to architect Jenkins in the cloud for scale
- How to configure multiple Jenkins masters
- Preparing AWS environment and CLI configuration
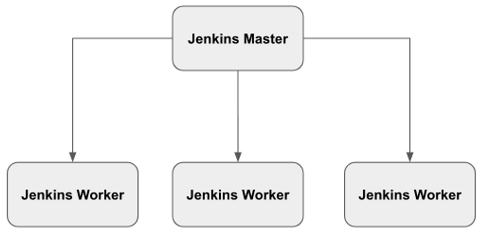
In a distributed microservices architecture, you may have multiple services to build, test, and deploy on a regular basis. Hence, having multiple build machines makes sense. While you can always run Jenkins in a standalone mode, running all builds on a central machine may not be the best option and will result in having a single point of failure (a single Jenkins server cannot handle the entire load for larger and heavier projects). Fortunately, Jenkins can also be configured to run distributed builds across a fleet of machines/nodes by setting up a master/worker cluster as shown in Figure 3.1.
Jenkins uses a Master-Worker architecture to manage distributed builds. Each component has a specific role: