This chapter covers:
- Symmetric Encryption, a cryptographic primitive to hide communication from observers
- Authenticated Encryption, the secure evolution of symmetric encryption.
- The popular authenticated encryption algorithms.
- Other types of symmetric encryption.
This is where it all began: the science of cryptography was first and foremost invented to fill our need to hide information. Encryption is what pre-occupied most of the early cryptographers: "How can we prevent observers from understanding our conversations?". While the science and its advances first bloomed behind closed door, benefiting the governments and their military only, it has now opened and spread throughout the world. Today, encryption is used everywhere to add a sense of privacy and security in the different aspects of our modern lives. In this chapter we’ll find out what encryption really is, what types of problem it solves and how today’s applications makes use of this cryptographic primitive.
For this chapter you’ll need to have read:
- Chapter 3 on Message Authentication Codes.
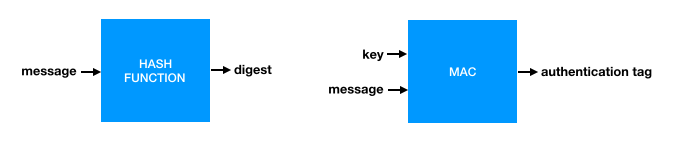
So far we’ve talked about hash functions and message authentication codes (MACs). These two constructions have distinctive interfaces that we recapitulate in figure 4.1.
Figure 4.1. The interfaces of the hash function and the message authentication code.
We will now attempt to introduce one as equally important cryptographic primitive: authenticated encryption.