Chapter 28. Practical auditing in SQL Server 2008
In SQL Server 2008 Enterprise Edition, instance- and database-level audit is now built into the Database Engine with its own set of instance- and database-level objects—Server Audit and Server Audit Specification at the instance level, and Database Audit Specification at the database level.
SQL Server 2005 introduced event notifications and data definition language (DDL) triggers as mechanisms for auditing DDL statements, but coverage of events wasn’t complete. There was no support for auditing access to data, and there was no tool support available in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Generating audit event s in SQL 2008 is extremely lightweight compared to previously available mechanisms, and is based on the new extended events infrastructure, which is designed to have an extremely low overhead even for large numbers of events. It also allows much finer-grained event filtering.
Note
All of the new audit features described in this chapter require SQL Server 2008 Enterprise or Developer Edition, and aren’t available in lower editions.
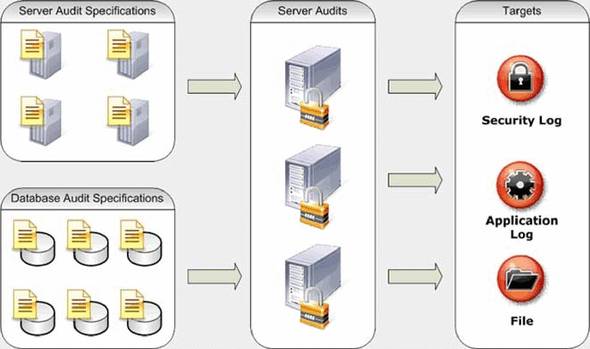
In SQL Server 2008, all events are now auditable using the new audit objects, including those not available via event notifications in previous versions of SQL Server. Configuration is greatly simplified with built-in tool support in SSMS. Figure 1 gives an overview of the various audit objects.