If you want to know how to automate running Terraform, this chapter is for you. Until now, I have assumed you are deploying Terraform from your local machine. This is a reasonable assumption for individuals and even small teams, as long as you are using a remote-state backend. On the other hand, large teams and organizations with many individual contributors may benefit from automating Terraform.
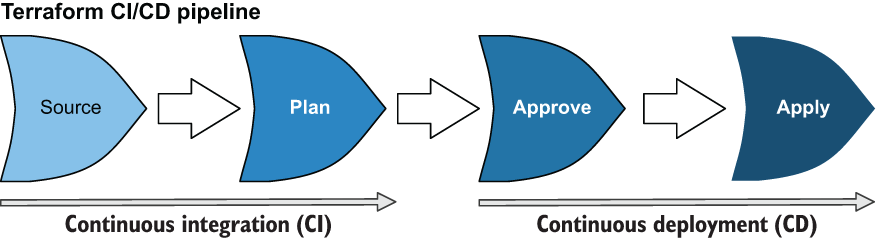
In chapter 6, we discussed how HashiCorp has two products to automate running Terraform: Terraform Cloud and Terraform Enterprise. These products are basically the same; Terraform Cloud is simply the software as a service (SaaS) version of Terraform Enterprise. In this chapter, we develop a continuous integration / continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline to automate deploying Terraform workspaces, modeled after the design of Terraform Enterprise. The stages of the CI/CD pipeline are shown in figure 12.1.