chapter three
3 Shallow Transfer Learning for NLP
This chapter covers:
- Using pretrained word embeddings in a semi-supervised fashion to transfer pretrained knowledge to a problem
- Using pretrained embeddings of larger sections of text, e.g., sentences, paragraphs, documents, in a semi-supervised fashion to transfer pretrained knowledge to a problem
- Using multi-task learning to develop better performing models that also more effectively transfer to other tasks
- Modifying target domain data to reuse knowledge from a resource-rich source domain, i.e., domain adaptation
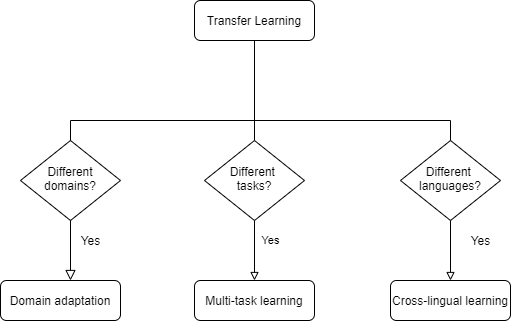
In this chapter, we will cover some prominent shallow transfer learning approaches and concepts. This allows us to explore some major themes in transfer learning, while doing so in the context of relatively simple models of the class of eventual interest, i.e., shallow neural networks. Several authors have suggested various classification systems for categorizing transfer learning methods into groups[1][2][3]. Roughly speaking, categorization is based on whether transfer occurs between different languages, tasks or data domains. Each of these types of categorization is usually correspondingly referred to as cross-lingual learning, multi-task learning and domain adaptation. These are visualized in Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1. Visualizing categorization of transfer learning into multi-task learning, domain adaptation and cross-lingual learning.